What is Virtualization
Virtualization
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of something such as a computer system, server. Instead of using physical hardware for each system or resource, virtualization allows multiple systems or functions to run on a single physical machine.
Hypervisor
A hypervisor (sometimes called a virtual machine monitor, or VMM) is software that creates, runs, and manages virtual machines (VMs) on a physical computer. It acts as a middle layer between the hardware and the operating systems running in the VMs.
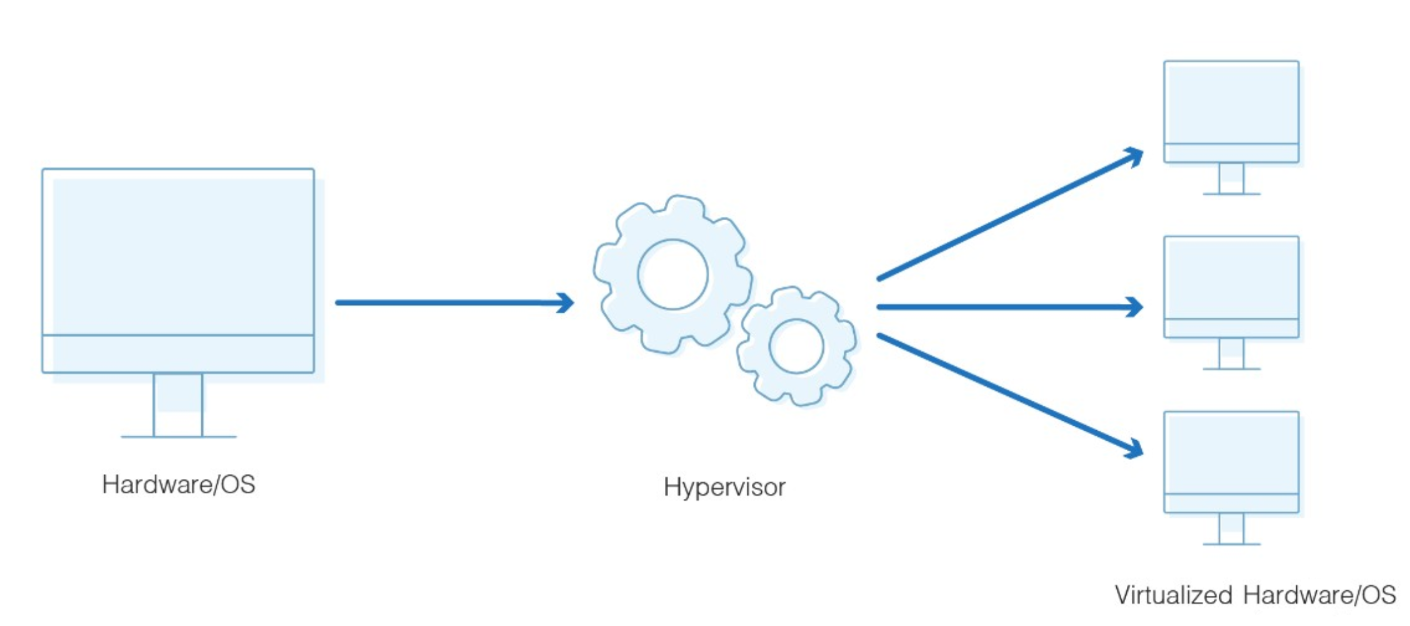
Examples:
Hyper V
Oracle VirtualBox
VMware Workstation
Parallels Desktop (Mac)
Virtual Machine
A Virtual Machine (VM) is a software-based computer — it runs like a real physical computer but exists inside another computer (called the host).
Key Components:
Guest OS: The operating system running inside the VM (e.g., Ubuntu Linux).
Host OS: The operating system of the actual physical computer (e.g., Windows).
Hypervisor: Software that creates and runs the VM (e.g., VirtualBox, VMware, KVM).
ISO File
ISO file (also called an ISO image) is a digital copy of an entire optical disc, such as a CD, DVD, or Blu-ray. It’s a single file that contains all the data and file system structure exactly as it was on the original disc.
In Simple Terms:
Think of an ISO file as a zip of a CD/DVD — but not just the files, it includes the boot information, file system, and even the layout of the original disc.
What Is It Used For?
Installing operating systems like Linux, Windows, or macOS (most Linux distros like Ubuntu, CentOS, Kali, etc. are distributed as ISO files)
Creating bootable USB drives
Running virtual machines (e.g., installing Linux in VirtualBox or VMware)
Archiving or backing up discs