If Else In Go Lang
Decision Making Statement In GO language
At some point we do take some decisions in our life similarly in the world of programming languages we have to take a lot of decisions and to serve those purpose we have these statements which help us in taking the decisions while coding.
Go language has 2 type of decision making statements.
- IF - ELSE
- Switch
We will be learning about IF-ELSE in This one.
IF-ELSE
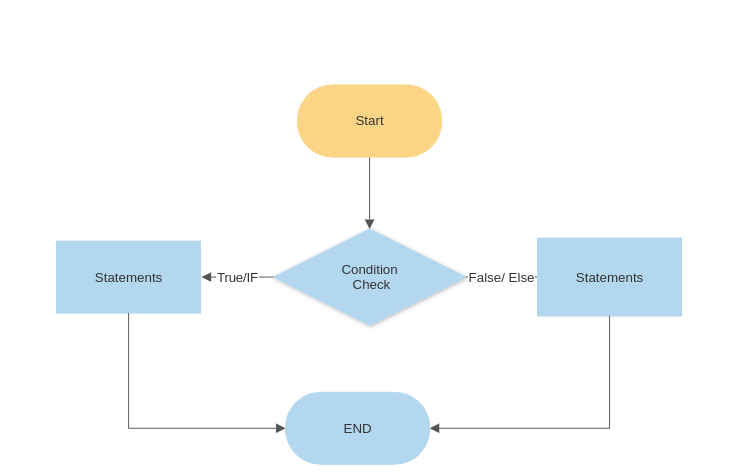
If else statement help us in making decisions based of true or false values of the condition. Here is simple example for the same. Let’s say you want to make coffee so you need to have some coffee powder. and If not then you have to bring it.
So the statement goes like
If < You Have Coffee Powder>
Make Coffee
Else
Bring some Coffee Powder
Here is a flow diagram to understand the same.
It’s not mandatory to else with if You can use if you can just end the program after if only.
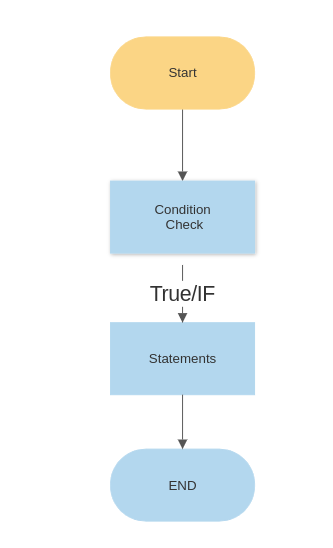
so the statement goes like
If < You Have Coffee Powder>
Make Coffee
Here is a flow diagram to understand the same.
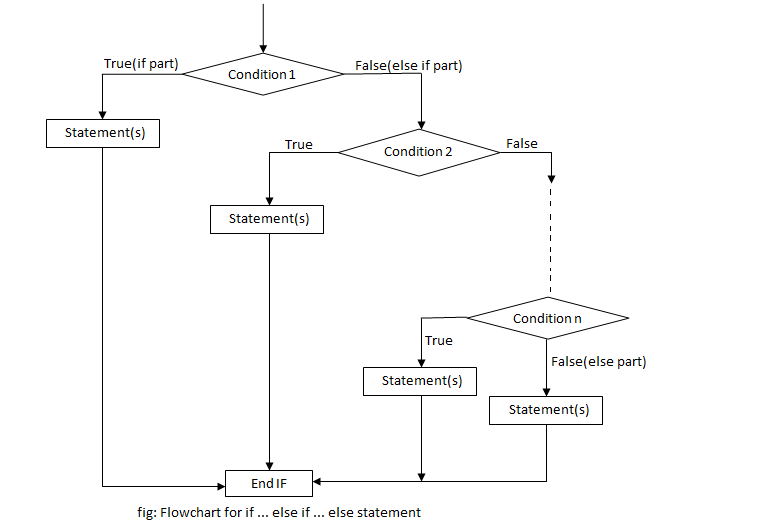
And in the last comes the if-else-if-else... part so here we can use more then one condition in a program for example.
If < Is it Monday>
Yes It's monday
Else If < It it Tuesday>
Yes It's Tuesday
Else If < Is it Wednesday >
Yes It's wednesday.
Else If < Is it Thursday >
Yes It's Thursday.
Else If < Is it Friday >
Yes It's Friday.
Else If < Is it Saturday >
Yes It's Saturday.
else
Yes It's Sunday.
Here is the flow diagram to understand the same.
Let’s checkout the IF-Else statement Syntax in GO lang.
if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else{
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
Syntax for using only IF.
if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
Syntax for using only IF-ELSE-IF-ELSE…
if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else if <initialization>; <condition> {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else{
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
initialization -> In This step we can assign or create a variable that can be used in the if-else hierarchy it’s not mandatory to pass the initialization step but don’t forget to add ; if you are defining.
If you are defining some variable in initialization step then it will not be visible outside the defined if-else hierarchy.
Now if you are using () in if block then you can not use the initialization step.
if ( <condition> ) {
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
else{
statements 01
statements 02
statements 03
...
...
statements N
}
NOTE :() In Condition is not mandatory and else statement is also not mandatory you can skip it if it’s not required. Another thing to note is that { should be written right after the condition you can not start { in the next line doing so will lead to error unexpected newline, expecting { after clause
So
if <condition> {
...
}
is correct syntax where.
if <condition>
{
}
is considered as wrong as { is in the next line of the if clause.
Doc was written in this livestream [Learn Go Day 08] and [Learn Go Day 10]